
Project for ClimateHack.AI 2023-24 in collaboration with Open Climate Fix.
Accomplishments
- Top 3 Submission from the University of Toronto
- Represented the University of Toronto at the International Finals at Harvard
- Finished 5th place overall, beating out teams such as CMU, Harvard, UIUC, etc
You can view the slides we used for the presentation here: Climate Hack 2023 Final.pdf
Challenge
ClimateHack.AI 2024
Motivation
- Electricity system operators ensure in real time that electricity can always be supplied to meet demand and prevent blackouts, but intermittent renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, introduce significant uncertainty into the grid’s power generation forecasts.
- To account for this uncertainty, electricity system operators maintain a spinning reserve based on non-renewable energy sources (e.g. natural gas) that can quickly ramp up to meet any shortfalls.
- More accurate near-term solar power generation forecasts would allow grid operators to reduce this use of non-renewables and cut emissions by up to 100 kilotonnes per year in Great Britain and on the order of 50 megatonnes per year worldwide by 2030.
Challenge
- In the 2023-24 competition, Open Climate Fix challenged our participants to develop accurate, efficient machine learning models for predicting solar power generation at the level of individual sites up to four hours ahead.
- Over 600 gigabytes of EUMETSAT satellite imagery, Deutscher Wetterdienst numerical weather predictions, ECMWF air quality forecasts and historical solar power generation data collected from live PV systems in the UK were made available to participants to build their models.
- All in all, 3,900+ models were uploaded by competition participants to the DOXA AI platform for evaluation, and the contributions of the competition will support the solar power nowcasting research of Open Climate Fix.
- Find out more about this year’s challenge on the competition page.
Dataset
Most important features
- Weather:
- Diffusive shortwave radiation (
aswdifd_s) - Direct shortwave radiation (
aswdir_s) - Cloud cover (%)
- High cloud cover (
clch) - Medium cloud cover (
clcm) - Total cloud cover (
clct)
- High cloud cover (
- Relative humidity (%) at 2 meters (
relhum_2m)
- Diffusive shortwave radiation (
- Time:
- Only evaluated between sunrise and sunset
Embeddings
import torch
from torch import nn
import math
class SinusoidalEmbedding(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, freqs):
super().__init__()
self.register_buffer("freqs", freqs)
def forward(self, input):
if input.shape[-1] != 1 or (input.ndim == 1 and input.shape[0] == 1): # otherwise crashes when B=1
input = input.unsqueeze(-1)
emb = input.float() * self.freqs
emb = torch.cat([emb.sin(), emb.cos()], dim=-1)
if emb.ndim == 2:
emb = emb.unsqueeze(1)
return emb
class FourierEmbedding(SinusoidalEmbedding):
def __init__(self, embedding_dim, period=1):
assert embedding_dim % 2 == 0
half_dim = embedding_dim // 2
# freqs = 2 * torch.pi * torch.arange(half_dim)
freqs = 2*torch.pi / period * 2**torch.arange(half_dim)
super().__init__(freqs)TimeEmbedding class is used to embed time-related features (month and hour) using Fourier embeddings. This helps the model capture periodic patterns in the data.
class TimeEmbedding(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, month_emb_dim = 16, hour_emb_dim = 16):
super().__init__()
self.month_emb = FourierEmbedding(month_emb_dim, 1.)
self.hour_emb = FourierEmbedding(hour_emb_dim, 24.)
def forward(self, time):
# (B, 2)
return torch.cat([self.month_emb(time[:, 0]), self.hour_emb(time[:, 1])], axis=-1)Model
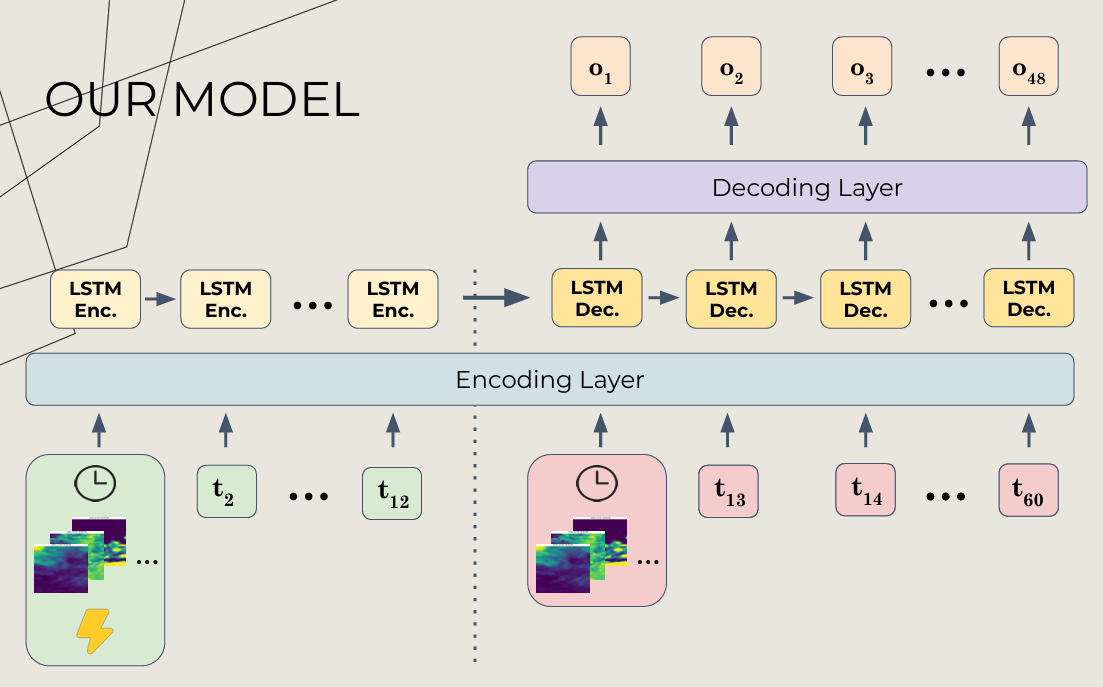
Our model is an Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) encoder-decoder architecture
class BaseLSTM(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, enc_model, dec_model, inp_emb, dropout=0.2, **kwargs):
# Initialize the parent class
super().__init__()
self.enc_model = enc_model # Encoder model
self.dec_model = dec_model # Decoder model
self.inp_emb = inp_emb # Input embedding layers
# Determine which features to use based on kwargs
self.used = [kwargs.get(f'use_{k.replace("-", "_")}', True) for k in ['pv', 'satellite-hrv', 'satellite-nonhrv', 'aerosols', 'weather', 'time', 'site']]
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(p=dropout) # Dropout layer for regularization
def emb_input(self, features):
# Extract the PV feature and other features
pv, *features, index = features
# Apply the corresponding embedding to each feature and return the embedded features along with the index
return (pv, *[emb(feat) for feat, emb in zip(features, self.inp_emb)], index)
def start_input_state(self, features, index):
raise NotImplementedError
def next_input_state(self, i, out, features, index, target=None):
raise NotImplementedError
def output_state(self, i, out, last_out, prediction=False):
# This method should be implemented by subclasses to define the output state
raise NotImplementedError
def forward(self, features, target, criterion):
# Embed the input features
*features_emb, index = self.emb_input(features)
# Get the initial hidden state from the encoder
_, tup = self.enc_model(self.dropout(self.start_input_state(features_emb, index)))
# Initialize the last output with padding
last_out = F.pad(features[0][:, -1, None], (0, self.dec_model.proj_size - 1), 'constant', 0)
loss = 0
# Iterate over the sequence length (48 time steps)
for i in range(48):
# Get the output and hidden state from the decoder
out, tup = self.dec_model(self.dropout(self.next_input_state(i, last_out, features_emb, index, target)), tup)
# Get the final output state
out = self.output_state(i, out, last_out)
loss += criterion(out.squeeze(-1), target[:, i].squeeze(-1))
# Update the last output
last_out = out
# Return the average loss
return loss / 48
def predict(self, features):
# Get the batch size, device, and dtype from the features
batch_size = features[0].shape[0]
device = features[0].device
dtype = features[0].dtype
# Embed the input features
*features_emb, index = self.emb_input(features)
# Get the initial hidden state from the encoder
_, tup = self.enc_model(self.dropout(self.start_input_state(features_emb, index)))
# Initialize the last output with padding
last_out = F.pad(features[0][:, -1, None], (0, self.dec_model.proj_size - 1), 'constant', 0)
# Initialize an empty tensor to store predictions
predictions = torch.empty(batch_size, 0, self.dec_model.proj_size, dtype=dtype, device=device)
# Iterate over the sequence length (48 time steps)
for i in range(48):
# Get the output and hidden state from the decoder
out, tup = self.dec_model(self.dropout(self.next_input_state(i, last_out, features_emb, index)), tup)
# Get the final output state
last_out = self.output_state(i, out, last_out, prediction=True)
# Append the output to the predictions tensor
predictions = torch.cat([predictions, last_out.unsqueeze(1)], axis=1)
# Rearrange the predictions tensor and return it
return rearrange(predictions, 'b t d -> d b t').squeeze(0)Full LSTM Model:
class FullLSTM(BaseLSTM):
def __init__(self, weather_features=None,
share_weights=False,
hidden_dim=512,
time_emb_dim=16,
site_emb_dim=30,
weather_emb_dim=64,
norm_type='batch',
pos_emb_dim=16,
wmo_emb_dim=16,
dropout=0.2,
time_emb_method='fourier',
pos_emb_method='learned',
inc_last=True,
teacher_forcing=False,
**kwargs): # uncertainty, model_diff, truncated
nn.Module.__init__(self)
# Determine if the last output should be included in the input
self.inc_last = inc_last or share_weights
total_emb_dim = int(self.inc_last)
self.teacher_forcing = teacher_forcing
####### TIME EMBEDDING ########
self.time_emb = nn.Identity()
if kwargs['use_time']:
if time_emb_method == 'fourier':
# Use Fourier embeddings for time features
self.time_emb = TimeEmbedding(time_emb_dim // 2, time_emb_dim // 2)
elif time_emb_method == 'learned':
# Use learned embeddings for time features
self.time_emb = nn.Linear(12 + 31 + 24, time_emb_dim)
total_emb_dim += time_emb_dim
####### WEATHER EMBEDDING ########
self.weather_emb_layer = nn.Identity()
if kwargs['use_weather']:
self.uses_wmo = 'ww' in weather_features
weather_features = [x for x in weather_features if x != 'ww']
if norm_type == 'batch':
# Use batch normalization for weather features
norm_layer = nn.Sequential(
Rearrange('b t c h w -> (b t) c h w'),
nn.BatchNorm2d(len(weather_features)),
Rearrange('(b t) c h w -> b t c h w', t=6),
)
if norm_type == 'global':
# Use global normalization for weather features
norm_layer = normalize_weather_layer(weather_features)
self.weather_emb_layer = nn.Sequential(
norm_layer,
nn.Flatten(start_dim=2),
nn.Linear((len(weather_features)) * WEATHER_SIZE ** 2, weather_emb_dim),
)
total_emb_dim += weather_emb_dim
if self.uses_wmo:
print('USES WMO')
self.wmo_emb_layer = nn.Embedding(100, wmo_emb_dim)
total_emb_dim += wmo_emb_dim
####### SITE EMBEDDING ########
self.site_emb = nn.Identity()
if kwargs['use_site']:
# Use embeddings for site features
self.site_emb = nn.Embedding(993, site_emb_dim)
total_emb_dim += site_emb_dim
####### POS EMBEDDING ########
if pos_emb_method == 'learned':
# Use learned positional embeddings
self.pos_emb = nn.Embedding(60, pos_emb_dim)
elif pos_emb_method == 'fourier':
# Use Fourier positional embeddings
self.pos_emb = PositionalEmbedding(pos_emb_dim)
elif pos_emb_method == 'none':
# Use zero positional embeddings
self.pos_emb = lambda x: torch.zeros(tuple(x.shape) + (1,) * (x.ndim == 1) + (0,), dtype=x.dtype, device=x.device)
total_emb_dim -= pos_emb_dim
total_emb_dim += pos_emb_dim
# Determine if uncertainty should be included in the model
uncertainty = kwargs['distribution'] != "none"
# Initialize the encoder LSTM
encoder = nn.LSTM(total_emb_dim - inc_last + 1, hidden_dim, proj_size=1 + uncertainty, batch_first=True)
if share_weights:
# Share weights between encoder and decoder
decoder = encoder
else:
# Initialize the decoder LSTM
decoder = nn.LSTM(total_emb_dim, hidden_dim, proj_size=1 + uncertainty, batch_first=True)
super().__init__(encoder, decoder, [self.weather_emb, self.time_emb], dropout=dropout, **kwargs)
self.kwargs = kwargs
# Initialize the predictor based on the distribution type
self.predictor = (TruncEM if self.kwargs['truncated'] else NormEM)(**self.kwargs)
def weather_emb(self, feature):
# Process weather features through the weather embedding layer
if self.uses_wmo:
emb = self.weather_emb_layer(feature[:, :, :-1])
emb = torch.cat([emb, self.wmo_emb_layer(torch.mode(feature[:, :, -1].flatten(start_dim=-2)).values.to(torch.int32))], axis=-1)
else:
emb = self.weather_emb_layer(feature)
return emb
def forward(self, features, target, criterion):
# Use the appropriate predictor based on the distribution type
if self.kwargs['distribution'] != 'none':
return super().forward(features, target, self.predictor)
return super().forward(features, target, criterion)
def start_input_state(self, features, index):
batch_size = features[0].shape[0]
# Create a tensor for the initial time steps
inp_t = torch.arange(12, device=features[0].device, dtype=torch.int32)[None].repeat(batch_size, 1) # B 12
# Concatenate the initial input features
inp_emb = torch.cat([features[0].unsqueeze(-1), features[1][torch.arange(batch_size)[:, None], (index + inp_t) // 12]], axis=-1)
if self.kwargs['use_time']:
inp_emb = torch.cat([inp_emb, features[2].repeat(1, 12, 1)], axis=-1)
if self.kwargs['use_site']:
inp_emb = torch.cat([inp_emb, features[3].repeat(1, 12, 1)], axis=-1)
inp_emb = torch.cat([inp_emb, self.pos_emb(inp_t)], axis=-1)
return inp_emb
def next_input_state(self, i, out, features, index, target=None):
batch_size = features[0].shape[0]
device = features[0].device
dtype = features[0].dtype
# Initialize an empty tensor for the next input state
inp_emb = torch.empty(batch_size, 1, 0, dtype=dtype, device=device)
# Create a tensor for the current time step
cur_t = torch.ones(batch_size, 1, device=device, dtype=torch.int32) * (i + 12)
if self.inc_last:
if (target is None) or (i == 0) or (not self.teacher_forcing):
# Use the output from the previous time step
inp_emb = torch.cat([inp_emb, out[:, None, [0]]], axis=-1)
else:
# Use the target from the previous time step
inp_emb = torch.cat([inp_emb, target[:, [i - 1], None]], axis=-1)
# Concatenate the next input features
inp_emb = torch.cat([inp_emb, features[1][torch.arange(batch_size)[:, None], (index + i + 12) // 12]], axis=-1)
if self.kwargs['use_time']:
inp_emb = torch.cat([inp_emb, features[2]], axis=-1)
if self.kwargs['use_site']:
inp_emb = torch.cat([inp_emb, features[3]], axis=-1)
inp_emb = torch.cat([inp_emb, self.pos_emb(cur_t)], axis=-1)
return inp_emb
def output_state(self, i, out, last_out, prediction=False):
out = out[:, -1]
if self.kwargs['model_diff']:
# Normalize the output
out = out * 0.086264
# Combine the current and last output states
out = torch.cat([out[:, :1] + last_out[:, :1], (out[:, 1:]**2 + last_out[:, 1:]**2).sqrt()], axis=-1)
if prediction:
# Use the predictor to generate the final output
return self.predictor.predict(out)
return out