Note: This project is heavily based on the “Intro to Geospatial ML” workshop held at the Deep Learning Indaba 2023 found here: indaba-pracs-2023/practicals/geospatial_machine_learning.ipynb at geoai · deep-learning-indaba/indaba-pracs-2023 Parts of this tutorial are taken directly from there.
Working with Geospatial Data
There are two main ways to represent geospatial data:
- Vector: points, lines, polygons, etc.
- Each vector object is a geometry that can have multiple attributes. Such data is typically saved as a vector file (
Shapefile(.shp) andGeoJSON, among many) - You can use
shapelyto generate geometries and edit them - Usually, we use geopandas to read/analyze vector data
- Coordinate reference systems (CRS) take you from the geometric coordinates (numbers) to the earth’s surface. We can use GeoPandas to inspect the CRS and adjust the projection accordingly
- Each vector object is a geometry that can have multiple attributes. Such data is typically saved as a vector file (
- Raster: similar to images, it is represented as a grid of cells or pixels, each cell holds a value representing a value or measurement. Raster data is typically stored in formats such as
GeoTIFForNetCDF.- We like to use
rioxarray
- We like to use
Task
Task: Classify farm-level crop types in Kenya using Sentinel-2 satellite imagery.
- Input:
- The input includes 12 bands of observations from Sentinel-2 L2A: observations in the ultra-blue, blue, green, red; visible and near-infrared (VNIR); and short wave infrared (SWIR) spectra, as well as a cloud probability layer.
- The cloud probability layer is a product of the Sentinel-2 atmospheric correction algorithm (Sen2Cor) and provides an estimated cloud probability (0-100%) per pixel.
- Each pixel has measurements for 13 dates that cover the whole farming season.
- Output:
- Classification of each farm into one of 7 categories 1 Maize 2 Cassava 3 Common Bean 4 Maize & Common Bean (intercropping) 5 Maize & Cassava (intercropping) 6 Maize & Soybean (intercropping) 7 Cassava & Common Bean (intercropping)
- Validation: random train-validation split by farm IDs.
- Measure Performance: cross-entropy
Preprocessing
Let’s first do some data processing steps:
- remove pixels where cloud probability > 50%
- Split data into train/validation/test sets
- Verify no data leakage among these sets
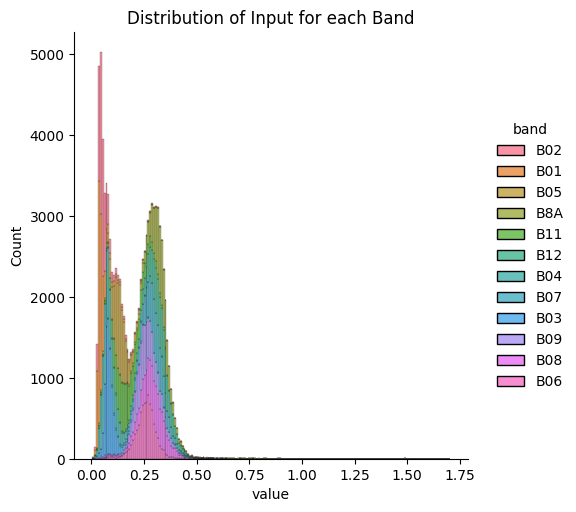
- Check the distribution of each channel or band
- Plot the farms by their labels in a map
- Visualize a farm’s Normalized Difference Vegetation Index over time
# Drop pixels that have a cloud cover greater than 50
df = df[df["CLD"] < 50]# Train/Validation/Test are the remaining rows
train_val_test = df[~df["field"].isin(deploy["field"])]
# Get the unique field IDs from the train/validation/Test rows
train_val_test_field_ids = train_val_test["field"].sample(frac=1).unique()
# Randomly select 80/10/10 split for train/val/test
val_field_ids = np.random.choice(train_val_test_field_ids, size=int(len(train_val_test_field_ids) * 0.1), replace=False)
test_field_ids = np.random.choice(list(set(train_val_test_field_ids) - set(val_field_ids)), size=int(len(train_val_test_field_ids) * 0.1), replace=False)
train_field_ids = list(set(train_val_test_field_ids) - set(val_field_ids) - set(test_field_ids))
# Create `train`, `val`, and `test` sets based on the validation field IDs
train = train_val_test[train_val_test["field"].isin(train_field_ids)]
val = train_val_test[train_val_test["field"].isin(val_field_ids)]
test = train_val_test[train_val_test["field"].isin(test_field_ids)]Plotting Distribution of each band:
Deep Learning Model (Seq2One Classifier)
Steps:
- Encode each image using a pre-trained encoder (ResNet18).
- Pass the sequence of encodings to a 3-layer Bi-directional GRU.
- Take the final concatenated output representation from the GRU and pass it through a fully-connected layer to predict the final class probabilities (7 classes).
- Use cross entropy as the loss function.
- Conduct data augmentation to regularize the model.
- Export the validation results
Dataset
@title Implement the `__len__` and `__getitem__` methods
class FieldSequenceDataset(Dataset):
"""
A dataset class for sequences of field images.
Attributes:
- X: Numpy array containing image sequences.
- y: Labels associated with each image sequence.
- classes: List of class names/labels.
- transforms: Optional data augmentation operations.
Methods:
- __len__ : Returns the length of the dataset.
- __getitem__ : Fetches a data sample for a given index.
- plot: Plots an image sequence from a given sample.
"""
def __init__(
self,
X,
y,
field_ids: List[int],
transforms: Optional[Callable] = None
) -> None:
"""
Initializes the dataset object.
Parameters:
- X: Numpy array containing image sequences of shape (num_samples, num_images, height, width, bands).
- y: Numpy array containing labels for each sequence.
- field_ids: List of indices to subset the dataset. Defaults to None (use all data).
- transforms: Optional data augmentation operations.
"""
# Define class labels
self.classes = [str(i) for i in range(1, 8)]
# Instead of slicing the data, store the indices
self.field_ids = field_ids
self.X = X
self.y = y
# Set the data augmentation transforms
self.transforms = transforms
def __len__(self) -> int:
"""Returns the number of samples in the dataset."""
return len(self.field_ids)
def __getitem__(self, index: int) -> dict[str, torch.Tensor]:
"""
Returns a data sample given an index.
Parameters:
- index: Index of the sample to fetch.
Returns:
Dictionary containing the image sequence and its associated label.
"""
# Use the field_ids to fetch the relevant data
sequence = self.X[self.field_ids[index]]
label = self.y[self.field_ids[index]]
# Convert them to PyTorch tensors
sample = {'image': torch.tensor(sequence, dtype=torch.float32), 'label': torch.tensor(label, dtype=torch.long)}
class SequenceClassificationModel(nn.Module):
"""
Neural network model for sequence classification tasks.
This model consists of a ResNet18 encoder, a bidirectional GRU, and a fully connected classifier.
Given an input sequence of images, it outputs class probabilities for each sequence.
Attributes:
- encoder: ResNet18 encoder for feature extraction from each image in the sequence.
- gru: Bidirectional GRU to model temporal dependencies in the sequence of features.
- fc: Fully connected layer to produce class probabilities.
"""
def __init__(self, in_channels, input_size, hidden_size, num_layers, num_classes):
super(SequenceClassificationModel, self).__init__()
self.encoder = ResNet18(in_channels, input_size)
self.gru = nn.GRU(input_size, hidden_size, num_layers, batch_first=True, bidirectional=True) # for modeling sequences
self.fc = nn.Linear(hidden_size * 2, num_classes) # for outputting class probabilities
def forward(self, x : torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
"""
Forward pass of the model.
Args:
- x (torch.Tensor): Input tensor of shape (batch_size, sequence_length, channels, height, width).
Returns:
- torch.Tensor: Output tensor of class probabilities with shape (batch_size, num_classes).
"""
batch_size, sequence_length, channels, height, width = x.shape
x = x.view(batch_size * sequence_length, channels, height, width)
x = self.encoder(x)
x = x.view(batch_size, sequence_length, -1)
x, _ = self.gru(x)
x = x[:, -1, :]
x = self.fc(x)
return x
class SequenceAugmentationPipeline(nn.Module):
"""
A data augmentation pipeline for sequences of images.
This module defines a set of transformations that are applied consistently across
all images in a sequence. This ensures that the spatial relationship between
images in a sequence remains consistent after augmentation.
Attributes:
- hflip: Random horizontal flip transformation.
- vflip: Random vertical flip transformation.
- rotate: Random rotation transformation.
"""
def __init__(self) -> None:
"""
Initialize the augmentation pipeline with desired transformations.
"""
super(SequenceAugmentationPipeline, self).__init__()
self.hflip = K.RandomHorizontalFlip()
self.vflip = K.RandomVerticalFlip()
self.rotate = K.RandomRotation(degrees=30)
def forward(self, input: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
"""
Apply the transformations consistently across each image in the sequence.
Parameters:
- input (torch.Tensor): Input tensor of shape (batch_size, sequence_length, bands, height, width).
Returns:
- torch.Tensor: Augmented tensor with the same shape as input.
"""
# Extract the shape parameters for the transformations from the first image
# in the sequence. This ensures consistent augmentation across all images.
hflip_params = self.hflip.forward_parameters(input[:, 0, ...].shape)
vflip_params = self.vflip.forward_parameters(input[:, 0, ...].shape)
rotate_params = self.rotate.forward_parameters(input[:, 0, ...].shape)
# Apply the transformations to each image in the sequence.
transformed_seq = []
for image in input.unbind(dim=1):
image = self.hflip(image, hflip_params)
image = self.vflip(image, vflip_params)
image = self.rotate(image, rotate_params)
transformed_seq.append(image)
# Combine the transformed images back into the sequence format.
output = torch.stack(transformed_seq, dim=1)
return output
class SequenceClassificationTask(LightningModule):
"""
Lightning module for the sequence classification task.
This module wraps the SequenceClassificationModel for training, validation, and testing.
It also handles data augmentation using the SequenceAugmentationPipeline.
Attributes:
- model: The sequence classification model.
- loss_fn: Loss function for classification.
- learning_rate: Learning rate for the optimizer.
- aug: Data augmentation pipeline for training sequences.
"""
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, in_channels=14, num_layers=3, num_classes=7, learning_rate=0.001):
"""
Initialize the lightning module.
Parameters:
- input_size (int): Size of the input to the GRU.
- hidden_size (int): Size of the GRU hidden state.
- in_channels (int, optional): Number of input channels to the model. Defaults to 14.
- num_layers (int, optional): Number of GRU layers. Defaults to 3.
- num_classes (int, optional): Number of classification classes. Defaults to 7.
- learning_rate (float, optional): Learning rate for the optimizer. Defaults to 0.001.
"""
super(SequenceClassificationTask, self).__init__()
self.model = SequenceClassificationModel(in_channels, input_size, hidden_size, num_layers, num_classes)
self.loss_fn = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
self.learning_rate = learning_rate
# Define the data augmentation pipeline for training.
self.aug = SequenceAugmentationPipeline()
def forward(self, x):
"""
Forward pass through the model.
Parameters:
- x (torch.Tensor): Input tensor.
Returns:
- torch.Tensor: Model predictions.
"""
return self.model(x)
def training_step(self, batch, batch_idx):
"""
Defines a single step during training.
Parameters:
- batch (dict): Batch of data.
- batch_idx (int): Index of the batch.
Returns:
- torch.Tensor: Training loss.
"""
x, y = batch["image"], batch["label"]
# Apply data augmentation to the training data.
x = self.aug(x)
logits = self(x)
loss = self.loss_fn(logits, y)
# Log training loss to TensorBoard.
self.log("train_loss", loss)
return loss
def validation_step(self, batch, batch_idx):
"""
Defines a single step during validation.
Parameters:
- batch (dict): Batch of data.
- batch_idx (int): Index of the batch.
Returns:
- torch.Tensor: Validation loss.
"""
x, y = batch["image"], batch["label"]
logits = self(x)
loss = self.loss_fn(logits, y)
# Log validation loss to TensorBoard.
self.log("val_loss", loss)
return loss
def test_step(self, batch, batch_idx):
"""
Defines a single step during testing.
Parameters:
- batch (dict): Batch of data.
- batch_idx (int): Index of the batch.
Returns:
- torch.Tensor: Testing loss.
"""
x, y = batch["image"], batch["label"]
logits = self(x)
loss = self.loss_fn(logits, y)
# Log testing loss to TensorBoard.
self.log("test_loss", loss)
return loss
def configure_optimizers(self):
"""
Configures the optimizer(s) and learning rate scheduler(s).
Returns:
- Dict: Contains optimizer and learning rate scheduler information.
"""
optimizer = torch.optim.AdamW(self.model.parameters(), lr=self.learning_rate)
# Define a learning rate scheduler that reduces the learning rate when the validation loss plateaus.
scheduler = ReduceLROnPlateau(optimizer, patience=5)
return {
"optimizer": optimizer,
"lr_scheduler": {
"scheduler": scheduler,
"monitor": "val_loss",
},
}# Set training config
root = "./files"
experiment_name = "seq2one-poc"
gpu = 0
min_epochs, max_epochs = 3, 30
# Set the hyperparameters
batch_size = 64
learning_rate = 0.001
hidden_size = 128
num_layers = 3
early_stopping_patience = 15dm = FieldDataModule(root=root, batch_size=batch_size, workers=2)# Create the task with the sampled hyperparameters
task = SequenceClassificationTask(input_size=512,
hidden_size=hidden_size,
num_layers=num_layers,
learning_rate=learning_rate)
# Create a dedicated models' directory for saving the trial's best models
models_path = Path(f"./models/{experiment_name}/")
models_path.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
# Set the callbacks
checkpoint_callback = ModelCheckpoint(
monitor="val_loss",
dirpath=models_path,
filename=f"model-{{epoch:02d}}-{{val_loss:.2f}}",
save_top_k=1,
mode="min",
)
early_stopping_callback = EarlyStopping(monitor="val_loss",
mode="min",
patience=early_stopping_patience)
# Create a TensorBoard logger
logger = TensorBoardLogger("./tb_logs", name=experiment_name)
# Trainer definition
trainer = Trainer(
logger=logger,
accelerator='gpu',
devices=[gpu],
max_epochs=max_epochs,
min_epochs=min_epochs,
callbacks=[checkpoint_callback, early_stopping_callback],
precision=16
)
trainer.fit(model=task, datamodule=dm)checkpoint_callback.best_model_score.item()# Load your model
model = SequenceClassificationTask.load_from_checkpoint(trainer.checkpoint_callback.best_model_path,
input_size=512,
hidden_size=hidden_size)
model.eval()
model.freeze()
# Get the validation data loader
test_dl = dm.test_dataloader()
# Predict
all_logits = []
y_tests = []
with torch.no_grad():
for batch in test_dl:
inputs = batch['image']
y_test = batch['label']
logits = model(inputs)
all_logits.append(logits)
y_tests.append(y_test)
# Concatenate all the results
all_logits = torch.cat(all_logits, dim=0)
y_test = torch.cat(y_tests, dim=0)
# Get the probabilities
y_test_hat = torch.nn.functional.softmax(all_logits, dim=1)
from sklearn.metrics import log_loss
# Get the arrays
y_test_np = y_test.cpu().numpy()
y_test_hat_np = y_test_hat.cpu().numpy()
# Convert y_val to a binary label indicator format
y_test_bin = label_binarize(y_test_np, classes=[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6])
cross_entropy = log_loss(y_test_bin, y_test_hat_np)
print("Cross Entropy:", cross_entropy)Code Link
My full code can be found here: